 ANT-FS and FIT
ANT-FS and FIT
 ANT-FS and FIT
ANT-FS and FIT
The Flexible and Interoperable Data Transfer (FIT) protocol is designed specifically for the storing and sharing of data that originates from sport, fitness and health devices. The FIT protocol defines a set of data storage templates (FIT messages) that can be used to store information such as user profiles and activity data in files. It is specifically designed to be compact, interoperable and extensible.
ANT File Share (ANT-FS) is an extension of the ANT protocol that provides a robust framework for transferring files wirelessly between two devices. ANT-FS was designed for ultra low power, and can be used in coin cell battery operated devices on both sides of the link. ANT-FS is often used in display devices with storage capabilities, such as fitness watches, which collect real-time data from sensors and allow it to be downloaded by a PC at a later time. The ANT-FS network key has been reserved for use by ANT-FS devices.
To use ANT-FS in an interoperable way, refer to the ANT+ Sync Device Profile which specifies the channel parameters and other minimum requirements for interoperability.
The following example use case illustrates one way that the FIT protocol is used to transfer personal monitoring information acquired during exercise to an internet database.
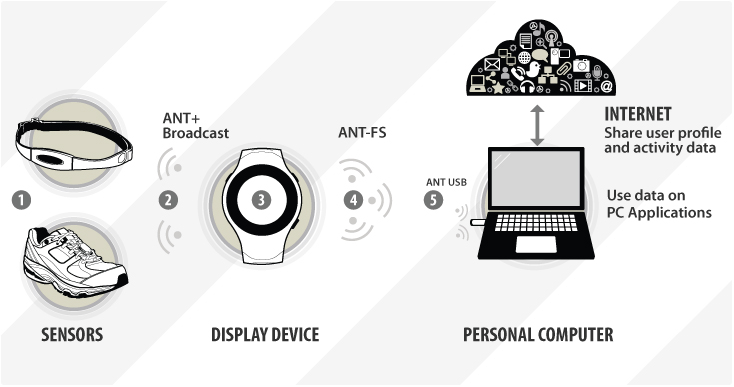
After the initial wireless sensor data is collected, the FIT protocol provides a consistent format allowing all devices in the subsequent chain to share and use the data.
Step 1: The FIT Protocol Document provides essential details on the FIT format. The document includes explanations of the binary file format including File Header, File CRC, Message Definition, FIT Base Types, Compressed vs. Normal Timestamp Headers as well as worked examples.
Step 2: An SDK is provided to simplify implementing FIT on the target platform. The SDK includes example programs to Encode and Decode FIT data in many popular programming languages. Sample .FIT files as well as a tool to convert back and forth to .csv are also included. Experimenting with these examples and demo apps is the next step to becoming familiar with FIT. The FIT SDK includes:
Step 3: The FIT File Types Document describes the predefined FIT File types which consist of common message groupings and methods for best practice. The FIT Profile (Profile.xls) lists all predefined FIT messages and FIT data types. This document is useful for understanding the content and format of particular messages. Custom messages and files may also be generated for application specific cases.
Step 1: The “ANT-FS Technical Specification” provides an overview of the operation of ANT-FS. Sections 1 – 8 are essential to understand the terminology and mechanisms involved. Note that ANT-FS applications typically use the ANT-FS network key (which may not be used by other applications).
Step 2: A great way of understanding how ANT-FS works is to use the ANT-FS PC tools and experiment with their different features. The “ANT-FS Reference Design User Manual” provides instructions for using the ANT-FS PC Host to connect to the ANT-FS PC client and download files from it. Walking through these will provide you a good idea of the steps involved on establishing a session through ANT-FS and transferring files between two devices.